Brain tumors are complex medical conditions that require specialized care and attention.This article will explore the various types of brain tumors which are Gliomas ,Meningiomas, Pituitary Adenomas, Medulloblastomas, Schwannomas, Lymphomas, Craniopharyngiomas ,Germ Cell Tumors ,Hemangioblastomas and Pineal Tumors.
Understanding Brain Tumors
Before delving into specific types, it’s crucial to understand what brain tumors are and how they develop.
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the brain or surrounding tissues. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can originate in the brain itself (primary tumors) or spread from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic tumors).
Classification of Brain Tumors
Brain tumors are typically classified based on:
- Origin of the tumor
- Location in the brain
- Grade (rate of growth and aggressiveness)
Let’s explore some of the most common types of brain tumors:
1. Gliomas
Gliomas are the most common type of primary brain tumor. They originate from glial cells, which support and protect nerve cells in the brain.
Types of Gliomas:
| Type | Characteristics | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Astrocytoma | Develops from star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes | I-IV |
| Oligodendroglioma | Arises from cells that produce myelin (the fatty covering of nerves) | II-III |
| Ependymoma | Forms in the lining of the ventricles or spinal cord | I-III |

Minimally invasive spine surgery techniques have revolutionized the treatment of some spinal gliomas, offering reduced recovery times and fewer complications.
2. Meningiomas
Meningiomas develop in the meninges, the protective layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. These tumors are often benign and slow-growing.

Characteristics of meningiomas:
- Usually benign (Grade I)
- More common in women
- Can cause symptoms by pressing on adjacent brain structures
Microsurgery for brain and spine is often employed in the treatment of meningiomas, allowing for precise removal of the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
3. Pituitary Adenomas
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that develop in the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. These tumors can affect hormone production and regulation.
Types of pituitary adenomas:
- Functioning adenomas (produce excess hormones)
- Non-functioning adenomas (do not produce hormones)

Endoscopic brain and spine surgery techniques have greatly improved the treatment of pituitary adenomas, allowing for minimally invasive removal through the nasal cavity.
4. Medulloblastomas
Medulloblastomas are fast-growing tumors that typically occur in children. They originate in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordination and balance.

Key features of medulloblastomas:
- Most common malignant brain tumor in children
- Requires aggressive treatment, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy
- Can spread to other parts of the central nervous system
Paediatric neurosurgery specialists are crucial in managing medulloblastomas and other brain tumors in children.
5. Schwannomas
Schwannomas develop from Schwann cells, which produce the insulating myelin sheath around nerves. The most common type is the vestibular schwannoma, also known as an acoustic neuroma.
Characteristics of schwannomas:
- Usually benign
- Can affect hearing and balance
- May cause facial numbness or weakness

Computed neuronavigation-assisted brain and spine surgery has greatly improved the precision and safety of schwannoma removal.
6. Lymphomas
Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphomas are rare tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) within the brain or spinal cord.
Risk factors for CNS lymphomas:
- Weakened immune system
- HIV/AIDS
- Organ transplant recipients
Treatment often involves a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
7. Craniopharyngiomas
Craniopharyngiomas are rare tumors that develop near the pituitary gland, often affecting both children and adults.

Symptoms of craniopharyngiomas:
- Visual disturbances
- Hormonal imbalances
- Headaches
- Cognitive changes
Awake brain surgery techniques may be employed in some cases to preserve critical brain functions during tumor removal.
8. Germ Cell Tumors
Germ cell tumors of the brain are rare tumors that primarily affect children and young adults. They typically develop in the pineal or suprasellar regions of the brain.
Types of germ cell tumors:
- Germinomas
- Non-germinomatous germ cell tumors
Treatment usually involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
9. Hemangioblastomas
Hemangioblastomas are rare, benign tumors that develop from blood vessels. They most commonly occur in the cerebellum, brainstem, or spinal cord.

Key features of hemangioblastomas:
- Often associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Can cause cysts to form
- May require regular monitoring and surgical intervention
Neuro vascular surgery techniques are often employed in the treatment of hemangioblastomas.
10. Pineal Tumors
Pineal tumors develop in or around the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain. These tumors can be benign or malignant and may affect the production of melatonin.
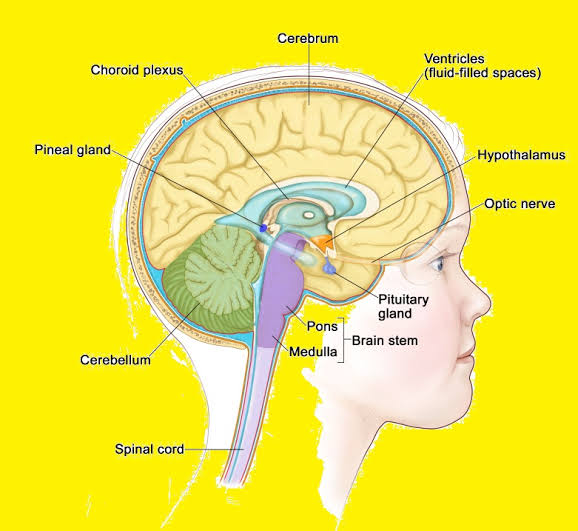
Types of pineal tumors:
- Pineocytomas (benign)
- Pineoblastomas (malignant)
- Mixed pineal tumors
Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the tumor type and grade.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis of brain tumors is crucial for effective treatment. Diagnostic tools may include:
- Neurological exams
- Imaging studies (MRI, CT scans)
- Biopsy
Treatment options vary depending on the tumor type, location, and grade. Common approaches include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapies
- Immunotherapy
At NeuroSpine Care, we offer advanced treatment options, including:
- Microsurgery for brain and spine
- Minimally invasive spine surgery
- Awake brain surgery
- Computed neuronavigation-assisted brain and spine surgery
Living with a Brain Tumor
A brain tumor diagnosis can be challenging, but with proper care and support, many patients can maintain a good quality of life. Important aspects of living with a brain tumor include:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Managing symptoms and side effects
- Emotional and psychological support
- Rehabilitation services (physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy)
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research in brain tumor treatment is focusing on:
- Targeted therapies
- Immunotherapy
- Gene therapy
- Improved imaging techniques
- Personalized medicine approaches
These advancements hold promise for more effective and less invasive treatments in the future.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of brain tumors is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. While a brain tumor diagnosis can be daunting, advances in medical technology and treatment approaches continue to improve outcomes for many patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the early signs of a brain tumor?
Early signs can vary but may include persistent headaches, seizures, vision problems, balance issues, and changes in cognitive function or personality. - Are all brain tumors cancerous?
No, brain tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). However, even benign tumors can cause serious symptoms due to their location and pressure on surrounding brain tissue. - How are brain tumors treated?
Treatment options depend on the tumor type, size, location, and grade. Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. - Can brain tumors be prevented?
Most brain tumors cannot be prevented. However, avoiding known risk factors, such as exposure to high doses of radiation, may help reduce the risk of certain types of brain tumors. - What is the prognosis for someone diagnosed with a brain tumor?
Prognosis varies widely depending on the tumor type, grade, location, and individual patient factors. Some brain tumors are highly treatable, while others may be more challenging to manage.
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your health care provider if you have persistent signs and symptoms that worry you.